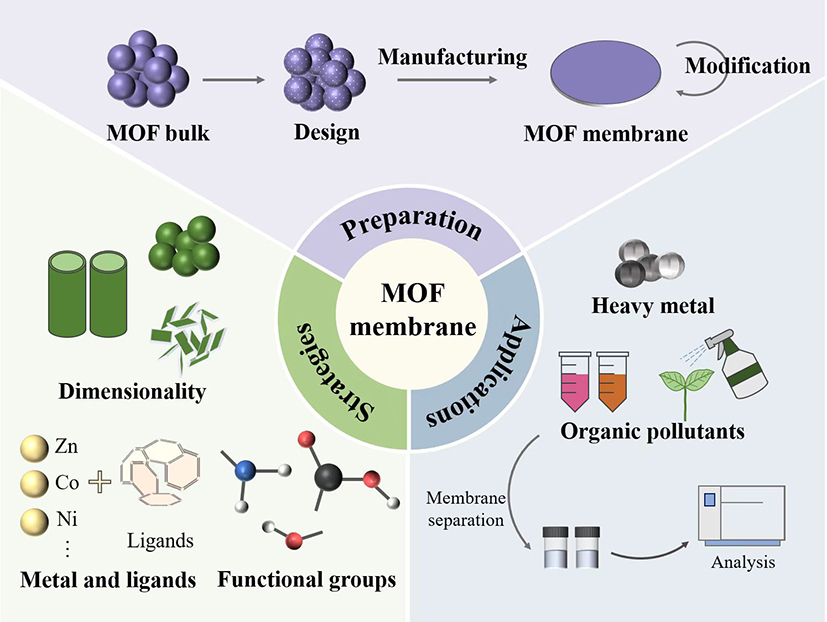
Recently, the Quality and Safety Group of the Institute of Vegetable and Flower Research, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) proposed new strategies to finely regulate the microstructure of MOFs nanocomposite membranes and enhance the adsorption and separation efficiency for chemical pollutants. The microstructures of MOFs membranes are finely tuned from the spatial latitude design, the optimized configuration of metal centers/ligands, and the selective modification of functional groups to enhance the pollutant-specific removal performance, which is innovatively illustrated. They systematically reveals the structure-effect correlation between structural features and application performance, introduces in detail the latest progress of composite membranes for the efficient removal of pollutants such as heavy metals, persistent organic pollutants and pesticide residues, and discusses in depth the future development trends and challenges. This review was publish in the Chemical Engineering Journal, IF=13.3.

Heavy metals, persistent organic pollutants, pesticide residues and other chemical pollutants are capable of transferring and accumulating toxicity through environmental waters, ecosystems and food chains, seriously threatening the quality and safety of edible agricultural products and the lives and health of the people. Metal-organic framework (MOFs) is a new type of porous organic nanomaterials with large specific surface area, rich pore space, and tunable structure, which can effectively deal with chemical contamination in the environment and edible agricultural products by combining with membrane separation technology. This review summarized the synthesis and preparation of MOFs nanocomposite membranes for the adsorptive removal of chemical pollutants, including the design strategy of MOFs crystals and structural units, the common preparation and modification methods of composite membranes. The regulatory mechanisms of MOFs nanocomposite membranes with different spatial dimensions, metal centers and ligands, and functional groups are elaborated in detail, and the conformational correlations between structural features and application properties are systematically revealed. Finally, the latest progress of composite membranes for efficient removal of pollutants such as heavy metals, persistent organic pollutants and pesticide residues is detailed, and the future development trends and challenges are discussed in depth. This review provides new insights into the precise design and utilization of the structure and properties of MOFs nanocomposite membranes, which is expected to provide a scientific basis for the research and development applications of MOFs nanocomposite membranes in the precise identification and adsorption of chemical pollutants and their efficient separation and removal.
Institute of Vegetable and Flower Research is the first to complete the paper. M.S. student Han Jiatong and Research Fellow Xu Donghui are the co-first authors of the paper. Research Fellow Liu Guangyang, Professor Wang Jing (Institute of Agricultural Quality Standards and Testing Technology, CA AS) and Research Fellow Xu Donghui are the co-corresponding authors. The research was carried out in the National Key Laboratory of Vegetable Biological Breeding and the Key Laboratory of Vegetable Quality and Safety Control of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, and was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program, the National Bulk Vegetable Industry Technology System, the Beijing Municipal Top-level Fund and the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences.
Original link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894724059990